What is a periodic table? Define Periodic table? define periodic table class 10 ।। define periodic table in chemistry ।। define periodic table of elements।। define periodic table class 8 ।। define periodic table family।। what is periodic table।। what is periodic table class 10th।। what is periodic table in chemistry।। what is periodic table in Hindi।। what is periodic table elements।। what is periodic table explain।।
What is a Periodic Table? Define Periodic Table?
A tabular arrangement of elements in groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) highlighting the regular trends in properties of elements is called a periodic table.
What is a Periodic Table? Define Periodic Table?
- The first attempts to classify elements into Metals and Non-metals was made by Lavoisier.
- After Lavoisier, Dobereiner also classified the elements.
- Dobereiner, a German chemist, grouped the elements in three (triads) in such a way that the middle element of the triad had both atomic mass and properties roughly equal to the average of the other two elements of the triads.
Newlands law of octaves
English Scientists also classified all known elements. He said that, Every eight element beginning from any element resembles the first element in its physical and chemical properties. This was known as the Law of Octaves.
Dmitri Mendeleev Periodic Table | Mendeleev Periodic Law
Mendeleev Periodic Law: The Properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses.
Key Points of Dmitri Mendeleev Periodic Table
- Mendeleev periodic tables are based on Atomic Masses.
- 63 elements were known in the time of Mendeleev.
- He arranges all known elements in vertical columns and horizontal rows.
- Horizontal rows are known as Periods.
- Vertical columns are known as Groups.
- Mendeleev Periodic Table was Published in a German Journal in 1872.
- In this periodic table, 8 groups and 7 Periods.
Merits of Mendeleev Periodic Table | Advantages of mendeleev periodic table
The merits / advantage of mendeleev periodic table are
- Grouping of elements.
- Gaps for undiscovered elements.
- Prediction of properties of undiscovered elements.
- Incorrect atomic mass corrected.
Example: Gold and Platinum.
Defects of mendeleev periodic table | Disadvantages of Mendeleev’s periodic table
Defects of mendeleev periodic table or Disadvantages of mendeleev periodic table are:
- Position of isotopes
Isotopes of an element are atoms of that element having similar chemical properties but different atomic masses.
What is an Isotope?
An element whose atomic number is the same but different mass number is called an isotope.
- Anomalous pair: some pair of elements do not follow Mendeleev principles.
Example: Argon and Potassium, Cobalt and Nickel, Tellurium and Iodine
- Grouping of chemically dissimilar elements.
- Separation of chemically similar elements.
- They do not explain the electron arrangement of elements.
- Position of Hydrogen.
Define Modern Periodic Law? What is Modern Periodic Law?
Modern Periodic law: Physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Key Points of modern periodic law
- Modern Periodic law was given by Henry Moseley in 1913.
- The Modern Periodic table is based on Atomic numbers.
- In this periodic table there are 18 vertical columns.
- And 7 horizontal rows known as periods.
- 18-en groups are divided into 4-blocks.
- S-block, P-block, d-block and f-block
Long form of Modern Periodic table
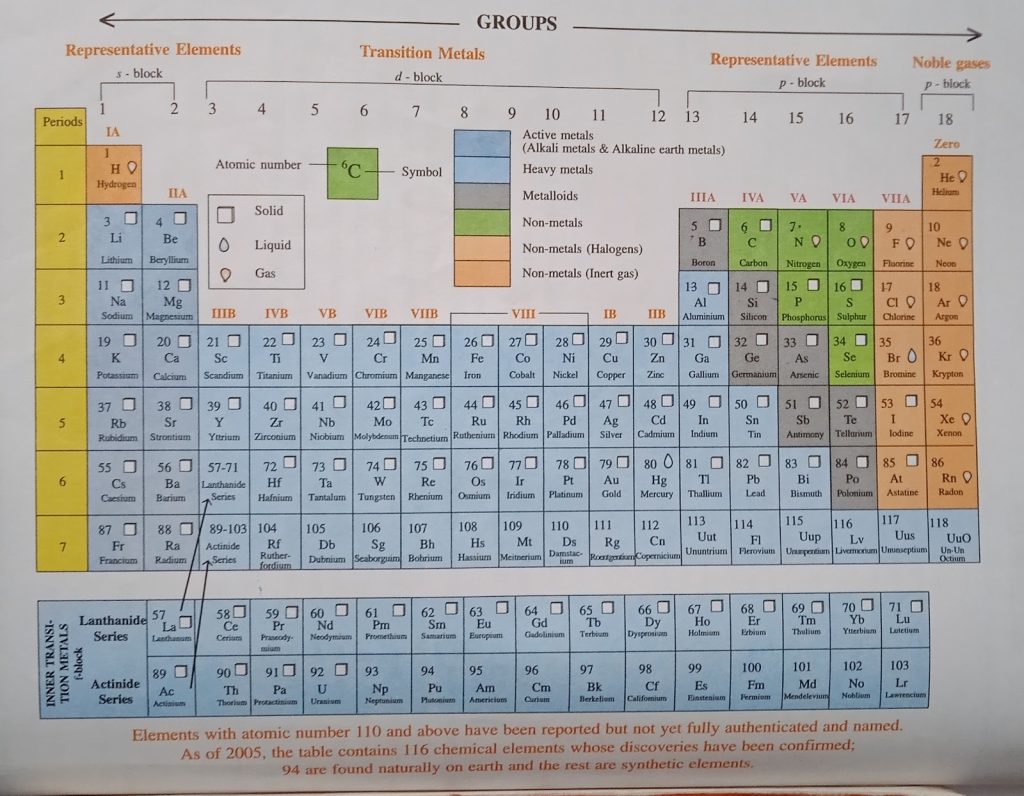
Group 1 or IA: Alkali metals – They form strong alkalis with water.
Group 2 or IIA: Alkaline earth metals – They form weaker alkalis as compared to group 1.
Group 13 or IIIA : Boron family – Boron is the
first member of the group.
Group 14 or IVA: Carbon family – Carbon is
the first member of the group.
Group 15 or VA:
Nitrogen family.
Group 16 or VIA: Oxygen family also known
as chalcogens meaning ore forming.
Group 17 or VIIA: Halogen family – The elements of this group form salts.
Group 18 (Zero group) – Elements of this
group are called the noble gases or inert gases. These elements have their outermost orbit complete. Due to stable electronic configuration they hardly react with other elements.
What is Periodicity? Explain Periodicity? Define periodicity?
Periodicity: The properties that reappear at regular intervals, or in which there is gradual variation (i.e. increase or decrease) at regular intervals, are called ‘Periodic properties’ and the phenomenon is known as the periodicity of elements.
Cause of Periodicity?
The cause of periodicity is the recurrence of similar electronic configuration i.e. having same number of electrons in the outermost orbit.
Read also: Dhartee kitne saal purani hai
What is a periodic table? Define Periodic table? define periodic table class 10 ।। define periodic table in chemistry ।। define periodic table of elements।। define periodic table class 8 ।। define periodic table family।। what is periodic table।। what is periodic table class 10th।। what is periodic table in chemistry।। what is periodic table in Hindi।। what is periodic table elements।। what is periodic table explain।।